HashMap的基层架构
HashMap底层的数据结构是:数组+链表+红黑树
数组查询效率高,链表插入删除效率高,HashMap的底层结构完美的解决了数组和链表的问题,使查询和插入、删除效率都很高。
当链表长度大于等于8并且数组长度大于等于64,链表长度就会转换为红黑树。如果红黑树的大小小于等于6,就会转换为链表。
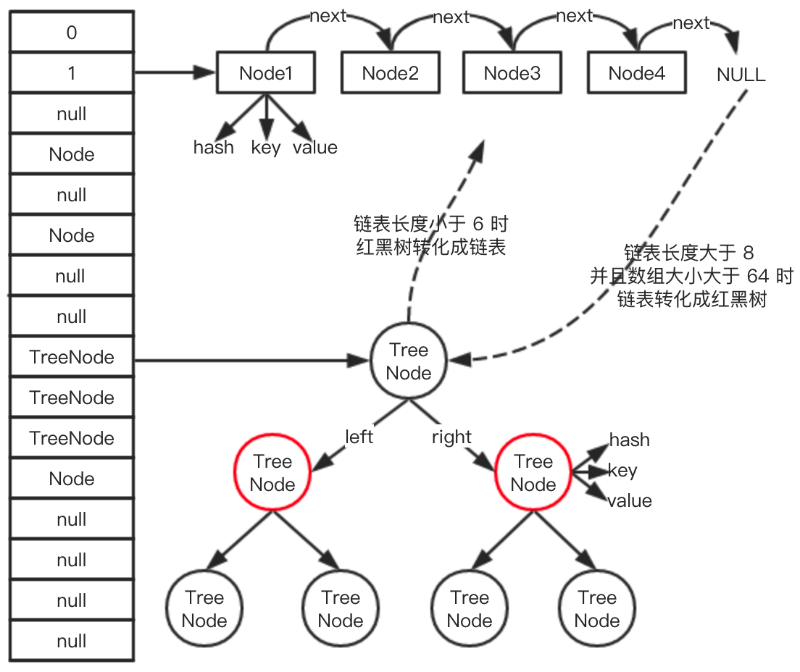
每一个节点保存的是Entry<Key,Value>的键值对。
HashMap的常见属性
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
* 初始容量
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
/**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
* 最大容量
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
* 负载因子默认值,扩容条件
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* 桶上的链表长度大于等于8时,链表转化成红黑树
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
/**
* 桶上的红黑树大小小于等于6时,红黑树转化成链表
*/
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
/**
* 当数组容量大于 64 时,链表才会转化成红黑树
*/
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
/**
* The table, initialized on first use, and resized as
* necessary. When allocated, length is always a power of two.
* 存放数据的数组
*/
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
/**
* Holds cached entrySet(). Note that AbstractMap fields are used
* for keySet() and values().
*/
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
/**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
* HashMap的大小
*/
transient int size;
/**
* 记录迭代过程中 HashMap 结构是否发生变化
*/
transient int modCount;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
* 扩容条件
* tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);数组大小接近2的幂次方。
* resize();数组大小 = 数组容量 * 0.75
* @serial
*/
int threshold;
/**
* The load factor for the hash table.
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor;
链表的节点存储结构
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
红黑树的节点
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
增加操作
对HashMap的操作实际上是对数组、链表与红黑树的操作。
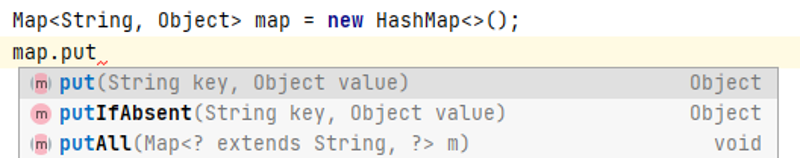
上图的这三种方法,都是在最底层的增加操作方法的基础上封装其他功能来实现的。
put 为我们最常用的增加操作的方法,
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
putIfAbsent 为当key已经存在时不去改变value的值
@Override
public V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
//相对于put(key,value),调用putVal时仅改变了第四个参数为true。
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, true, true);
}
putAll 就是批量添加,多了一个循环。
final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) {
int s = m.size();
if (s > 0) {
if (table == null) { // pre-size
float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F;
int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
if (t > threshold)
//tableSizeFor 扩容
threshold = tableSizeFor(t);
}
//resize 方法进行扩容
else if (s > threshold)
resize();
//循环一个一个添加
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) {
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict);
}
}
}
三种方法底层都调用了final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict)这个方法,具体也看一下这个方法。
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* 参数:
* @param hash值
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent 如果为true,就不改变已经存在的value值
* @param evict 如果为false,则逐出表,表处于创建模式。
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
//table==null时进行初始化操作,n为table表的长度
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
//判断table[(n-1)&hash]这个位置是否为空,若为空则直接加入节点。
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
//table[(n-1)&hash]该位置不为空,解决Hash冲突
//临时变量
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//如果key的hash和值都相等,把当前节点赋值给临时变量
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
//已经存在该节点key
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
//红黑树增加节点方法putTreeVal
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTre;
else {
//链表尾插
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
//当链表的长度大于等于 8 时,链表转红黑树
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
//判断是否要覆盖value
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
//判断是否需要扩容
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
evict 这个变量当在map构造器传入指定map初始化的时候是false,其他情况为true,也即其他构造器创建map之后再调用put方法,该参数则为true。
增加 Key,Value 步骤如下:
1、空数组有无初始化,没有的话初始化;
2、如果通过key计算的hash,数组table[hash]位置为空,则直接加入新元素;
3、如果hash冲突,解决方法:链表或红黑树;
4、如果是红黑树,调用红黑树的新增方法putTreeVal;
5、如果是链表,把新元素追加到队尾。
6、根据onlyIfAbsent来判断是否需要需改value值
7、判断是否需要扩容。
链表的新增:
链表的新增就是把新节点追加到链表尾部,如同LinkedList。
当链表长度大于等于 8 时,此时的链表就会转化成红黑树,转化的方法是:treeifyBin,此方法有一个判断,当链表长度大于等于 8,并且整个数组大小大于 64 时,才会转成红黑树,当数组大小小于 64 时,只会触发扩容,不会转化成红黑树。
红黑树的新增:
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTre;
final TreeNode<K,V> putTre { Class<?> kc = null; boolean searched = false; //找到根节点 TreeNode<K,V> root = (parent != null) ? root() : this; for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) { int dir, ph; K pk; //p.hash 值大于 h,说明 p 在 h 的右边。 if ((ph = p.hash) > h) dir = -1; //p.hash 值小于 h,说明 p 在 h 的左边。 else if (ph < h) dir = 1; //判断key是否已经存在 else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk))) return p; //自己实现的Comparable的话,不能用hashcode比较了,需要用compareTo else if ((kc == null && (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) || (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) { if (!searched) { TreeNode<K,V> q, ch; searched = true; if (((ch = p.left) != null && (q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null) || ((ch = p.right) != null && (q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null)) return q; } dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk); }
TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
//找到和当前hash值相近的节点(该节点的左右子节点有至少一个为空的)
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
Node<K,V> xpn = xp.next;
//生成新的节点
TreeNode<K,V> x = map.newTreeNode(h, k, v, xpn);
//将新节点放在当前子节点为空的位置上
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
//建立当前节点与新节点的关系
xp.next = x;
x.parent = x.prev = xp;
if (xpn != null)
((TreeNode<K,V>)xpn).prev = x;
//balanceInsertion 对红黑树进行着色或旋转,以达到更多的查找效率
//moveRootToFront 把算出来的root放到根节点上。
moveRootToFront(tab, balanceInsertion(root, x));
return null;
}
}
}
红黑树的新增还是比较难理解的。
着色:新节点总是为红色;如果新节点的父亲是黑色,则不需要重新着色;如果父亲是红色,那么 必须通过重新着色或者旋转的方法,再次达到红黑树的5个约束条件
旋转: 父亲是红色,叔叔是黑色时,进行旋转
如果当前节点是父亲的右节点,则进行左旋
如果当前节点是父亲的左节点,则进行右旋
红黑树的5个基本原则:
1、节点是红色或黑色
2、根是黑色
3、所有叶子都是黑色
4、从任一节点到其每个叶子的所有简单路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点
5、从每个叶子到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点
查找
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
//计算key的hash值,调用getNode获取key对应节点
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
//如果第一个节点的hash等于key的hash,并且equals相等,直接返回第一个节点
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
//红黑树类型,红黑树的查找方法
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
//链表的查找方法
do {
//自旋查找
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
大致分为一下几步:
1、计算key的hash值,通过hash来定位数组索引,判断数组的第一个节点的hash和key与我们传入的key是否相等。如果相等则直接返回该节点。
2、判断当前节点有无next节点,判断节点类型来选择红黑树查找方法和链表查找方法。
3、红黑树查找方法。
4、链表自旋查找方法。
红黑树的查找方法
1、从根节点递归查找。
2、根据红黑树节点左小右大的原则,比较hash值来查找节点。
3、一直自旋到定位到该节点的位置为止。
删除操作
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
//定位要删除的节点
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
//红黑树查找要删除的节点
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
//链表循环查找要删除的节点
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
//删除节点操作
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)
//红黑树删除节点操作
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)
//数组该索引位置第一个节点删除
tab[index] = node.next;
else
//链表删除节点
p.next = node.next;
++modCount;
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
删除操作也是先定位要删除的节点,根据节点类型,红黑树和链表采用各自的方法。
然后删除该节点。
关于hash(key)函数
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
根据传入的key值来计算hash值。计算-取模。 可参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/zhengwang/p/8136164.html
文章来源:blog.csdn.net/Zhangxg0206/article/details/111310927
注意:本文归作者所有,未经作者允许,不得转载